In today's data-driven world, the terms "row and column" might seem trivial, but they form the backbone of data organization and management. Rows and columns are not just confined to spreadsheets; they are crucial components of databases, data tables, and any structured data format. Understanding the intricacies of rows and columns is essential for efficient data handling, whether you're managing a small business inventory or analyzing large datasets for scientific research.
Rows and columns are the pillars of data structuring, enabling users to input, process, and analyze data effectively. A row represents a single data record, while a column represents a field within that record. Together, they create a grid-like structure that makes it easier to view and manipulate data. This concept is not only fundamental to spreadsheets but also to relational databases and various data management systems.
As we delve deeper into the world of data, mastering the concepts of rows and columns becomes imperative. This article will explore their significance, applications, and best practices in data management. From setting up a basic spreadsheet to understanding complex database systems, we'll cover all you need to know about rows and columns in a comprehensive, engaging manner.
Read also:Brandon Frazier A Stellar Figure In Ice Skating
Table of Contents
- What is a Row and Column?
- The History and Evolution of Rows and Columns
- Why are Rows and Columns Important in Data Management?
- Applications of Rows and Columns in Various Fields
- How to Use Rows and Columns in Excel?
- Rows and Columns in Database Systems
- Best Practices for Organizing Data with Rows and Columns
- Common Mistakes to Avoid with Rows and Columns
- Advanced Techniques for Manipulating Rows and Columns
- How Do Rows and Columns Affect Data Visualization?
- Tools and Software for Managing Rows and Columns
- The Future of Rows and Columns in Data Management
- Case Studies: Success Stories Using Efficient Row and Column Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is a Row and Column?
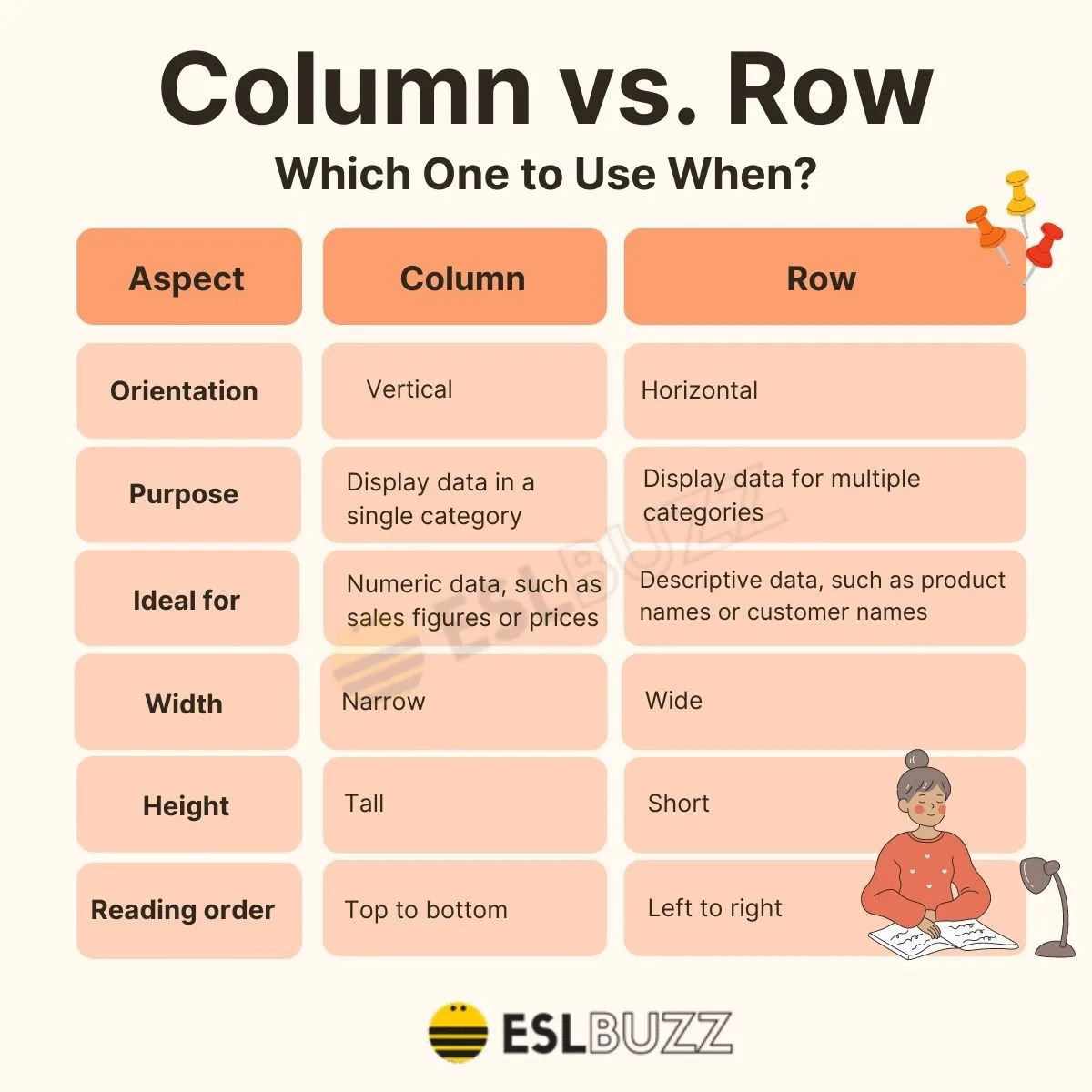
Rows and columns are integral components of any structured data format. In a spreadsheet or database, a row is a horizontal series of cells that represent a single data record. For example, in a table of customer information, each row might contain data for a single customer, including their name, address, and contact details. A column, on the other hand, is a vertical series of cells that represent a single field or attribute across multiple records. In the same customer table, columns could represent fields like 'Name,' 'Address,' 'Phone Number,' and so on.
The concept of rows and columns is foundational in data management because it allows for the logical structuring and querying of data. This structure supports operations such as sorting, filtering, and summarizing data efficiently. In more sophisticated databases, rows and columns are often referred to as 'tuples' and 'attributes' respectively, highlighting their role in relational database management systems (RDBMS).
The History and Evolution of Rows and Columns
The origins of rows and columns can be traced back to ancient times when people used papyrus scrolls and clay tablets to record data in a structured format. However, the modern concept of rows and columns emerged with the advent of the spreadsheet in the late 20th century. The first electronic spreadsheet, VisiCalc, was developed in 1979 and revolutionized the way businesses approached data management. It introduced the grid layout that became the standard for organizing and analyzing data.
As technology advanced, so did the complexity of data management systems. Relational databases, developed in the 1970s, extended the use of rows and columns beyond spreadsheets. They allowed for more sophisticated data operations and set the stage for the development of SQL (Structured Query Language), which uses rows and columns as fundamental elements of data manipulation.
Why are Rows and Columns Important in Data Management?
Rows and columns are vital to data management for several reasons:
- Organization: They provide a clear and logical structure for data, making it easier to input, navigate, and understand.
- Efficiency: Rows and columns facilitate quick data retrieval and manipulation, thanks to their structured format.
- Consistency: They ensure that data is stored uniformly, reducing errors and discrepancies.
- Scalability: This structure can easily accommodate growing datasets, making it suitable for both small and large-scale data management.
In summary, rows and columns are indispensable for the efficient handling and analysis of data, whether in simple spreadsheets or complex database systems.
Read also:The Astonishing Life Of The Worlds Tallest Woman A Journey Of Height And Heart
Applications of Rows and Columns in Various Fields
The application of rows and columns extends across multiple fields, each with its unique requirements and challenges. Some notable applications include:
- Business: Rows and columns form the basis of financial models, inventory management systems, and customer databases.
- Education: They are used to maintain student records, manage class schedules, and analyze academic performance.
- Healthcare: In medical databases, rows and columns help manage patient records, treatment histories, and billing information.
- Science and Research: Researchers use this structure to organize experimental data, track research progress, and publish findings.
- Government: Rows and columns are employed in census data collection, tax records, and public policy analysis.
In each field, the fundamental principles of using rows and columns remain the same, but the specific applications may vary.
How to Use Rows and Columns in Excel?
Excel is one of the most popular tools for working with rows and columns. Here's how to make the most of its features:
Setting Up a Spreadsheet
When setting up a spreadsheet, start by defining the purpose of your data. Use rows to represent individual records (such as transactions or employees) and columns to represent attributes or fields (such as dates or salaries).
Data Entry and Formatting
Ensure data consistency by using validation tools and formatting options. Excel provides features like drop-down lists and conditional formatting to help maintain data integrity.
Data Analysis
Excel offers powerful tools for analyzing data organized in rows and columns. Use formulas, pivot tables, and charts to summarize and visualize your data effectively.
By mastering these features, you can maximize the potential of Excel for data management and analysis.
Rows and Columns in Database Systems
In database systems, rows and columns play a critical role in the storage and retrieval of data. They are the foundation of relational databases, which organize data into tables where each row is a record and each column is a field. This structure enables databases to efficiently perform complex queries and operations.
Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS)
RDBMS like MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server use tables with rows and columns to store data. The relationship between these tables allows for data integration and complex querying, making RDBMS a powerful tool for managing large datasets.
Normalization
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database to minimize redundancy. It involves structuring tables and columns to ensure data is stored logically and efficiently, often by breaking down tables into smaller, related tables.
SQL Queries
SQL (Structured Query Language) is used to interact with databases, allowing users to select, insert, update, and delete data within tables. Understanding how to construct SQL queries is essential for leveraging the power of rows and columns in databases.
By understanding the role of rows and columns in databases, users can better manage and manipulate data, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Best Practices for Organizing Data with Rows and Columns
To optimize the use of rows and columns in data management, consider these best practices:
- Consistency: Use consistent naming conventions for columns to avoid confusion and ensure clarity.
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to ensure that the data entered into each cell is accurate and relevant.
- Documentation: Provide clear documentation for the structure and purpose of your rows and columns to help others understand and use the data effectively.
- Backup and Security: Regularly back up your data and implement security measures to protect it from unauthorized access or loss.
Adhering to these practices will help maintain data integrity and usability, making it easier to achieve your data management goals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Rows and Columns
While rows and columns are straightforward concepts, there are common pitfalls to avoid:
- Inconsistent Data Entry: Ensure that data is entered consistently to avoid errors and discrepancies.
- Overcomplicating Structure: Keep the structure simple and logical to make data easier to manage and understand.
- Ignoring Data Validation: Failing to implement data validation can lead to data entry errors and unreliable results.
- Neglecting Documentation: Without proper documentation, others may struggle to understand the purpose and organization of your data.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure the efficient and accurate use of rows and columns in your data management efforts.
Advanced Techniques for Manipulating Rows and Columns
For those looking to take their data management skills to the next level, consider these advanced techniques:
Data Consolidation
Combine data from multiple sources or worksheets into a single table using tools like Excel's Consolidate feature or SQL JOIN operations.
Dynamic Arrays
Leverage dynamic arrays in Excel to automatically update and expand your data range as new data is added.
Advanced Filtering
Use advanced filtering techniques to extract specific data subsets based on complex criteria, enhancing your data analysis capabilities.
By mastering these advanced techniques, you can enhance your ability to manipulate and analyze data organized in rows and columns.
How Do Rows and Columns Affect Data Visualization?
Rows and columns are critical to effective data visualization. Their structure influences how data is presented in charts, graphs, and dashboards. Here's how they contribute to visualization:
- Clarity: A well-organized table with clear row and column labels helps ensure that visualizations accurately represent the data.
- Interactivity: Tools like pivot tables and slicers allow users to interact with data, providing dynamic insights and fostering deeper understanding.
- Customization: By organizing data effectively, users can create customized visualizations tailored to specific needs and audiences.
Understanding the relationship between rows, columns, and visualization can enhance the impact and effectiveness of your data presentations.
Tools and Software for Managing Rows and Columns
Numerous tools and software are available to help manage rows and columns effectively, each offering unique features and benefits:
Excel and Google Sheets
These spreadsheet applications are widely used for their ease of use and powerful data manipulation capabilities.
Database Management Systems
Systems like MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server offer robust features for managing large datasets using rows and columns.
Data Visualization Tools
Tools like Tableau and Power BI enable users to create compelling visualizations by leveraging structured data from rows and columns.
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific data management needs and the scale of your operations.
The Future of Rows and Columns in Data Management
As data management continues to evolve, rows and columns will remain fundamental components. However, advancements in technology are likely to influence their application and efficiency:
Future trends may include:
- Automation: AI and machine learning could automate many data management tasks, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- Integration: Seamless integration with other data sources and systems will become increasingly important for comprehensive data analysis.
- Visualization: Enhanced visualization techniques will continue to evolve, making it easier to interpret complex datasets.
By staying informed about these trends, data professionals can ensure they remain at the forefront of effective data management practices.
Case Studies: Success Stories Using Efficient Row and Column Management
Numerous organizations have achieved significant success by implementing efficient row and column management strategies. Here are a few examples:
Retail Giant's Inventory Management
By organizing their inventory data in a structured format using rows and columns, a major retail company was able to streamline its operations, reduce waste, and increase profitability.
University's Student Records System
A leading university revamped its student records management system by leveraging rows and columns to improve data accuracy and accessibility, enhancing both administrative efficiency and student satisfaction.
These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of mastering row and column management in various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the key differences between a row and a column?
Rows run horizontally and represent individual records, while columns run vertically and represent attributes or fields within those records. - How can I ensure data consistency in my spreadsheets?
Use data validation, consistent naming conventions, and regular audits to maintain data consistency. - What tools can I use for advanced data analysis with rows and columns?
Consider using tools like Excel, SQL databases, and data visualization software like Tableau for advanced analysis. - How do rows and columns impact data visualization?
They provide the structure necessary for creating accurate and effective visualizations by organizing data logically. - Can I automate data management tasks involving rows and columns?
Yes, automation tools and scripts can streamline repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. - What are some common mistakes to avoid with rows and columns?
Avoid inconsistent data entry, overcomplicating structure, ignoring data validation, and neglecting documentation.
Conclusion
Rows and columns are the unsung heroes of data management, providing the structure necessary for organizing, analyzing, and visualizing data effectively. By understanding their role and employing best practices, individuals and organizations can unlock the full potential of their data, driving informed decision-making and achieving greater success. As technology continues to advance, staying abreast of new developments and tools will ensure that rows and columns remain a powerful asset in the ever-evolving world of data management.
For further reading on data management and organization, visit Data.gov, a resourceful website offering insights and tools for data professionals.